Overactive Bladder, Symptoms, and Diagnoses
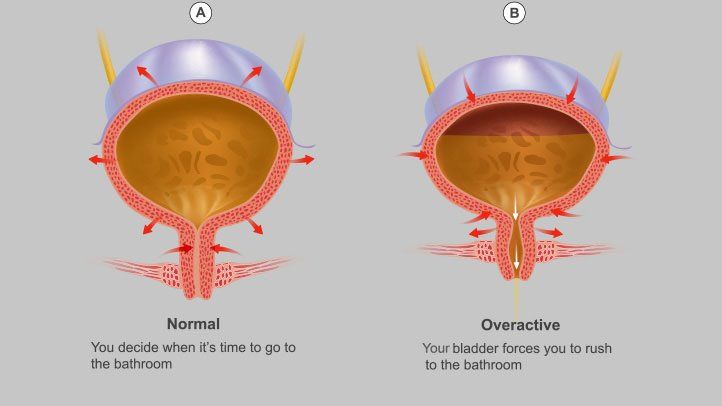
Overactive bladder is a medical condition that results in problems of bladder-storage functioning of the patient. Usually, the Overactive Bladder problem, in which patients feel a sudden urge to urinate, is quite common among patients with Multiple Sclerosis (MS). The most difficult and irritating aspect of the disease is that the urge to urinate might be quite difficult to restrain, and the Overactive Bladder may lead to involuntary loss of urine, which is called incontinence.
Problems of Patients with Overactive Bladder
There are two major problems that patients with Overactive Bladder suffer from. One is the problem in storing urine in the bladder, while the other is difficulty emptying or urinating. Doctors are yet to find out why only one of these two symptoms is noticed in a group of MS patients, while a bit of both can be noticed in others. A healthy bladder can store urine or empty at will. When the bladder is filled with enough urine, the brain sends warning signals to the bladder, requiring emptying. The muscles of the bladder wall coordinate with one another to decide whether to store or empty the content inside the bladder. As one muscle of the bladder contracts, the other gets relaxed.
Problem in Storing
If the nerve pathway inside the patient’s spine gets interrupted, their bladder muscles will contract even when a minimal amount of urine is accumulated inside the bladder. In severe conditions, usually, the patient fails to ‘hold on,’ and that patient’s medical condition is called Urinary Incontinence.
Problem in Emptying
Often patients with an Overactive Bladder suffer from difficulties in emptying. Problems can range from anything like poor flow during urination, interrupted and incomplete emptying, and different other variants of these problems. Sometimes, a significant amount of urine remains inside the bladder after the urination procedure is over. All these problems can be indicating the problem of the Overactive Bladder due to Multiple Sclerosis.
Symptoms of The Disease
If the problem of Overactive Bladder causes due by Multiple Sclerosis, the symptoms can be anything or everything among,
- Increased urinary frequency (8 or more times in 24 hours)
- Difficulty in controlling the urge to urinate
- Involuntary loss of urine immediately following an urge to urinate
- Waking up twice or more than that for urinating at night (nocturia)
Diagnosis of Overactive Bladder
To detect your problem, the doctor needs to rely on a number of clues, including:
- Your medical history
- Physical examination (mainly the abdomen and genitals)
- Testing urine samples to find out traces of blood or any other form of abnormalities
- Neurological tests to identify abnormal reflexes or sensory problems.
Special Tests
Doctors can decide to go for a few special tests to ensure the proper diagnosis of the medical problem and the right treatment. Such urodynamic tests are done to assess the functionality of your bladder and whether it can empty completely and steadily or not. Such tests can include measuring the rate of urine flow, measuring the amount of urine left in the bladder after urination, Testing bladder pressure, etc.
Treatment of Overactive Bladder
There are some behavioral interventions that doctors often recommend to manage an overactive bladder. These interventions play critical roles in reducing the frequency of urinary incontinence episodes. The interventions suggested by the doctor usually include,
- Losing Weight
- Consuming Enough Fluid
- Exercise of Pelvic Floor Muscle
- Scheduled Toilet Trip
- Absorbent Pads
- Intermittent Catheterization
- Bladder Training
Medicines
A few medicines can help the patient manage the symptoms of an overactive bladder and reduce the urge for urinary incontinence.
The list of such medicines includes:
- Tolterodine
- Oxybutynin
- Solifenacin
- Darifenacin
- Trospium
- Mirabegron
Other medicines are often used to put a check the number of incontinence episodes. Some of these medicines also have side effects like dry mouth and dryness of eyes, constipation, etc. But, the gel or skin patch versions of a few of these medicines have been proved to have a lesser amount of side effects.
Trending Health Topics
- ADHD
- Allergies
- Arthritis
- Bipolar Disorder
- Bunions
- Car Accidents
- Chron's Disease
- Common Cold
- COPD
- Depression
- Dry Skin
- Dry throat
- Eczema
- Fungal Infection
- GERD
- HIV/AIDS
- Hypertension
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriasis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Skin Disorders
- strep throat
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Uncategorized