Why Are My Feet Peeling After I Shower?
If you ask yourself, “Why are my feet peeling after I shower?” you are not alone.
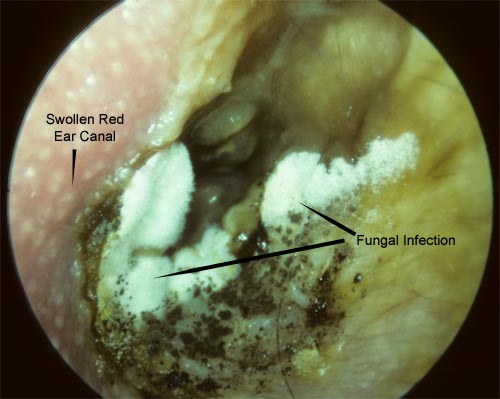
Otomycosis or, in other words, fungus in the ear, is a fungal infection of the external auditory canal. It is a common medical condition, caused by the fungus aspergillus or candida.
Ear is a favorable place for bacteria development, as it is likely to spread in dark, warm and humid environment. The disease is also referred to as Swimmers or Singapore ear, as it often occurs when water gets into the ear canal. The reason is that water washes off wax, which protects ears from infections.
Fungus may affect any person; however it is more spread in tropical climate. People suffering from diabetes or have decreased immune system are also at increased risk of being affected. Ear fungus is not a contagious infection; it also doesn’t spread to other parts of the body.
Otomycosis usually develops as any other fungal infection.
Below are the main signs and symptoms of the disease:
Otomycosis may be diagnosed by the visual examination with the otoscope. The diagnosis of the infection is confirmed by testing a swab.
The treatment involves the following actions:
The treatment usually lasts for 1-3 weeks. During the treatment, preventing measures should be taken. Thus, water shouldn’t get into the ears, swimming should be avoided and shower should be taken in shower cap. Ears shouldn’t be cleaned with cotton wool buds.
Here is the list of measures that can help prevent otomycosis:
Although ear fungus is not a life-threatening disease and is treated easily with over-the-counted medicines, it is not recommended to practice self-treatment, as only doctor can clean ears in a proper way and prescribe the most efficient medicines. Moreover, if you clean the ear wrongly, you may damage it and provoke further development of the infection.
If you ask yourself, “Why are my feet peeling after I shower?” you are not alone.
Medical Referral | Accident Attorney Referrals
Filter out the noise and nurture your inbox with health and wellness advice that’s inclusive and rooted in medical expertise.
MedicalReferral.com does not provide medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment.