Oral Cancer Symptoms, Early Signs, First Warning Signs of Mouth Cancer
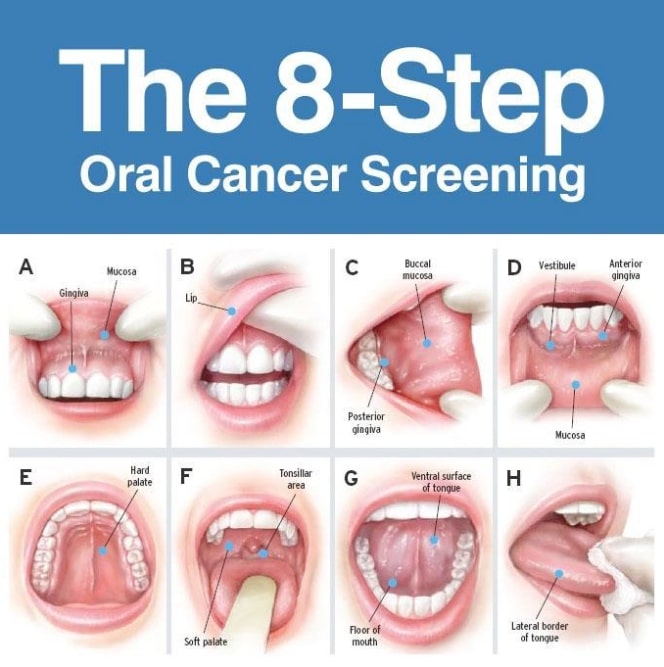
Cancer is an epidemic of modern times. People fear it more than other deadly diseases of its nature. Unfortunately, cancer can attack any body part, and oral structures are not excluded. Oral cancer has been trending as people’s lifestyles have been changing over time.
What passes through our mouths is not what used to pass in the mouths of our ancestors. People have invented so many types of foods, with most of them being sugary. The causes of oral cancer are more of what we know. Check them out hereof.
Oral Cancer Causes
Tobacco
Tobacco is a substance smoked by many around the world as a drug. The smoke has to pass through the mouth before it gets to the lungs, where it is absorbed. It has been said time and again that there are no benefits of smoking tobacco. For sure, you feel nice once you have that tobacco in your blood, but you lose a lot, including putting your body at risk of contracting chronic diseases. The worst-case comes in when tobacco is chewed instead of being smoked. Tobacco addiction also ensures that it has to be chewed or smoked daily, making the situation worse daily.
Alcohol
The alcohol that so many people pass in the oral cavity is just like all other foods. If alcohol can cause damages to the lungs, it can also affect oral health. Cancer is an extreme case caused by heavy drinking of alcohol. The risk of oral cancer is higher when a combination of alcohol and tobacco addiction is involved.
Poor Oral Hygiene
Cancer looks for places to hide. Areas in the mouth that are exposed will present the best thriving spots for cancer to start. If you have wounds in the mouth, those are the areas cancer will target. For that reason, you must check with your dentist for any persistent wounds that would need correction. Please do everything you can to ensure that your oral hygiene is at its perfect always.
HPV Virus
It’s a virus known to infect the moist linings and the skin. These moist skins include those of the vagina, the anus, throat, and mouth. Just by contact with an infected person, you can contract the virus. Sexual contact with the infected person can also cause HPV. This virus can, in rare cases, lead to abnormal growth of tissues around the oral linings leading to mouth cancer.
UV Rays
Sun rays can be harmful to the human body when they are taken in huge doses. The lips being the exterior oral structures, can experience abnormal growth if they are constantly exposed to UV light of the sun.
Early Signs of Oral Cancer
At the early stages, oral cancer may not produce symptoms. Most people can easily think they are suffering from mouth patches and white spots from dipping or oral ulcers and blisters from HPV. Since cancer can affect any of the working parts of the mouth, signs can appear on gums, tongue, tonsils, throat, the roof of the mouth, etc.
According to Health Line, “In the early stages, mouth cancer rarely causes any pain.” The lack of pain can make it difficult to notice that something is wrong. Here is a list of the early signs and symptoms of oral cancer.
Leukoplakia white patches in the mouth:
- Development of white and red patches in the mouth
- Recurring sore that doesn’t heal
- Swelling inside the mouth or thickening oral tissue
- Unusual oral bleeding (epistaxis)
- Chewing and swallowing problems
- Chronic sore throat
- Painful jaw and tongue movements or pain in the mouth
- Progressive swelling
- Unusual surface changes
- Sudden tooth mobility
- Speech problem
- Non-healing ulcers in the mouth or lips
- Prolonged hoarseness
- Unexplained numbness in the mouth
If you see any of these early symptoms of oral cancer, ensure that you see your doctor. Early and quick diagnosis helps in managing and limiting the spread of the growth in your mouth.
Other Symptoms of Oral Cancer
Mouth cancer has been linked to HPV, dipping or chewing tobacco, and excessive consumption of alcohol. The symptoms of mouth cancer may therefore be visible on the tongue, gums, and lips. When it is clearer that you have cancer cells developing in your mouth, you will likely experience the following signs of oral cancer.
White and red patches in mouth white and red patches in the mouth are associated with the development of malignant growth of cells in the mouth. Mouth cancer appears in different forms and can affect all parts of the mouth. White patches that rub off could be a sign of mouth cancer.
Red patches in the mouth:
- Leukoplakia white patches are common in people who dip or chew tobacco.
- It is evident as a grayish or white patch inside the mouth’s surface – gums, cheeks, the roof of the mouth, and even tongue.
However, according to Cancer Research UK, “A white or red patch in the mouth or throat does not necessarily mean cancer. A fungal infection called thrush can cause them. The white patches of thrush usually rub off, leaving a sore, red patch underneath.”
Red patches and spots may also be a sign of oral cancer. They may also be areas of abnormal cell growth. These are called erythroplakia and may present as oral mucosa lesions that present a bright-red velvety plaque.
The prescience of painless white and red patches should be taken seriously, and visit a dentist to look at the changes in the mouth and advice accordingly.
Thickening Lump jaw or cheek
A lump thickening in the oral tissue or soreness that does not heal or resolve itself within two weeks could be a sign of mouth cancer. It should be evaluated for further treatment to be sure if it’s cancer or not. A red hot lump that does not go away and keeps on becoming bigger in the neck can be attributed to cancer and should not be ignored.
- Lumps that come and go may not be a sign of cancer.
- A hot lump in the neck is likely to be a sign of infection rather than cancer.
- Cancerous lumps in the neck and jaw signify a swollen lymph node, a common symptom of oropharyngeal cancers.
The feeling of an Object in The Throat or Sore Throat
Do you feel like something is stuck in your throat all the time, when lying down or when swallowing? Feeling like something is stuck in the throat (dysphagia) can lead to difficulty swallowing saliva, and food is a sign of a serious infection. When the feeling remains for an extended period of time is an early warning sign of oral cancer.
Mouth cancer may spread to the esophagus and larynx and cause further symptoms. According to the American Cancer Society, one of the most common signs of esophageal cancer and possibly oral cancer is dysphagia. “The most common symptom of esophageal cancer is a problem swallowing, with a feeling like the food is stuck in the throat or chest, or even choking on food.”
Numbness or Pain on Tongue or Inside The Mouth
Numbness of the tongue or any other areas in the mouth such as chin, lips may be related to cancer. Loss of feeling in the mouth or areas of the face may be due to affected nerve endings.
Unexplained numbness around the mouth or inside the mouth, which doesn’t heal and keeps on recurring, needs to be reviewed. Numbness of the mouth is an early warning sign of oral cancer.
According to Dr. Chris of health hype, Paresthesia of the tongue is any abnormal sensation like numbness, tingling, or prickling (pins or needles feeling). The tongue is one of the most sensitive organs of the body. A sensation of temperature, pressure texture, and pain are often heightened on the tongue and capable of a unique sensory function taste (dysgeusia).
Swelling of The Mouth
Swelling of the chin, jaw or may occur elsewhere in the face leading to other complications that need to be reviewed as soon as possible since it is another early sign of oral cancer. Jaw swelling that makes dentures painful or fit poorly or the swelling of the mouth is an early sign of oral cancer.
“Stomatitis is a term used for a swelling mouth that disrupts a person’s ability to eat, talk and sleep. This can occur anywhere inside the cheeks, gums, tongue, lips, and palate.”
Ear Pain or Loss of Hearing
An earache that keeps on recurring even after antibiotic treatments and ear drops should be reviewed seriously since it is another known major early sign of oral cancer. Loss of hearing is a major fact that has been attributed as a sign of oral cancer. The loss of hearing may be partial or total. Thus any ear infection should be examined by a specialist for proper and timely redress.
According to the American society of clinical oncology, a sense of fullness or pain is caused by the buildup of fluid in the middle of the ear or trouble hearing. In some cases, hearing loss has been found as one of the major symptoms of oral cancer. Any changes and experiences should be looked at by a doctor who will look at and ask how long and how often one has been experiencing the symptoms. American family physician notes that the patients that smoke and take excess alcohol have higher risks of developing otalgia.
Oral Bleeding
Oral bleeding may be nose bleeding and mouth bleeding, which may be an indicator of oral cancer. Especially if the bleeding keeps recurring, it calls for a specialized review. Unusual bleeding, which has no explained causes, is an indicator of serious infection, which needs to look at by a doctor to address and recommend the best medication or advanced procedures to be taken.
American cancer society states, “bleeding in the mouth is often caused by mouth sores, gum (periodontal) diseases or low platelet count.” Canadian Dental Association also echoes this that the presence of blood regularly in the mouth should be the cause of concern and need to be evaluated to determine whether it is cancer or not.
Swallowing Problem, Speaking Problem, Breathing Problem, and Chewing Problems
When a tumor has developed in the sinuses or back of the neck, one may experience trouble breathing as a tumor grows. If the tumor happens at the back of the throat, swallowing food becomes a problem, an indicator of advanced cancer. Any changes in the neck and throat need to be reviewed and addressed appropriately.
According to the oral cancer foundation, difficulty swallowing (dysphagia) is one of the first symptoms of oral cancer due to tumor growth and narrowing the food passage. This symptom is usually common to those who have cancer of the gullet (esophagus). The other symptoms accompanying dysphagia are a regurgitation of food, vomiting, coughing, choking, and pain swallowing (odynophagia). American speech-language-hearing association states, “tongue cancer can cause a problem with some sounds,” which also is echoed by UK cancer research.
Loose Teeth
Loose tooth for no known cause is an early sign of oral cancer. In such a case, one should visit the dentist for a close examination to determine the actual cause of loose tooth, which can help seek medical remedies in the early stages of oral cancer, making it possible to avoid the cells multiplying to other or close tissues. Loose teeth for no apparent reason should be addressed early.
Changes in The Denture
Changes in the way the dentures fit on one another is another sign of oral cancer. Any changes in the structure of feeling discomfort of the denture should be alarming and call for doctors’ examination.
Gingivitis and preceding periodontitis are problems that involve the gums. Gingivitis (gum inflammation) occurs before periodontitis (gum disease). According to published research in cancer Epidemiology, Biomarkers & Prevention, these problems occur to many smokers. Periodontitis is also known to cause one loose tooth, and its effects are irreversible.
Persistent Sore on The Face
Sore that causes discomfort or is painfully sensitive on the face for a prolonged period of time is first oral cancer symptoms. Therefore, the persistent face sore calls for doctor review and advice to be able to prevent and address the causes. In cases where they are a sign of cancer, one can seek medication at early stages, which makes it treatable.
A lump on or in the face, nose, or mouth
Persistent Mouth Sore
A mouth sore which is recurring, is another sign of oral cancer. A mouth sore that comes as a result of unknown causes needs a doctor’s examination. The sores are major early signs of mouth cancer, more so to those who smoke and take more than 30 pints of alcohol in a week. Then, any mouth sore should be reviewed when there is still time to determine the cause and address it.
The Cancer Council Victoria attributes at least 75% of head and neck cancer to be caused by cigarettes and heavy drinking, which majorly causes a persistent sore or swelling in the mouth or jaw.
Persistent Pain in The Mouth
Persistent pain in the mouth is another most common sign of oral cancer. Unexplained mouth pain for an extended period of time or that keeps recurring is another major sign attributed to oral cancer.
Stomatitis is a term used for an inflamed and mouth sore that can disrupt a person’s ability to eat, talk, and to some extent, sleep. The overall effect of stomatitis is weight loss due to affected eating.
Persistent Sore Throat
Sore throat that keeps on recurring despite treatment is a common symptom of oral cancer. Sore throat is an indicator of an infection, and to many extents, it occurs to any person at least in one’s lifetime. But persistent and recurring sore throat even after treatment is an early sign of underlying advanced infection that has been attributed to oral cancer.
Sore throat refers to pain, itchiness, or irritation of the throat. A sore throat can affect people of all ages, but the risk is much more in children, smokers, allergic people, and those with a compromised immune system.
Speech Problem or Voice Changes
Speech that sounds quieter, husky, or as if one has cold or trouble pronouncing some words can also be attributed to oral cancer. Changes in speech for a period longer than two weeks and keep on recurring for some time are signs of oral cancer.
Muscular diseases that affect the jaws, teeth, and mouth can impair speech. According to the heart health newsletter, Speech is affected through pitch and quality of voice by abnormalities of the vocal cord, which include inflammation, polyps, cysts, and tumors.
Non- Healing Ulcers
Ongoing pain or discomfort in the mouth is a common sign of oral cancer. An ulcer (a broken skin area) inside the mouth that does not heal is attributed to cancer. Painless ulcers are one of the most common signs of oral cancer.
Mouth ulcers are painful oval sores that commonly appear in the mouth and heel themselves within a week or two with no need to visit a doctor. However, non-healing ulcers that may develop in the cheeks, lips, and tongue, especially those who drink alcohol, use tobacco products, and are affected with HPV, should visit the doctor. It is important to review mouth cancer while chances of survival are high.
Dramatic Weight Loss
Weight loss is a sign of many cancers; oral cancer hinders eating; thus, one may eat less due to mouth pain since it is painful and difficult to swallow. Therefore, extreme weight loss is a sign of advanced cancer; thus, if one loses a lot of weight and does not diet, should seek doctors’ advice.
According to Cancer Centre UK, oral cancer develops in the tissues of the mouth or throat and spread to squamous cells found in the mouth, which affects eating, swallowing, and chewing, which may lead to malnutrition which, if extended for some time, leads to dramatic weight loss.
Headache
A nuisance problem in the head that causes pain for a period of time is an indicator of an infection. Headache is a normal infection that occurs in people at one stage of life, which may not indicate cancer. Still, an extended headache for a longer period of time is also a sign of oral cancer.
Headache (cephalgia), according to WHO as “the pain in the head which accompany many diseases and conditions.” Reports by WHO states that 47% of adults worldwide will have experienced headaches within the year. Headache can be a standalone illness or a symptom of another condition.
Swollen Lymph Nodes / Glands
A common occurrence of swelling in the lymph glands is another sign of oral cancer. Lymph nodes filter and collect and destroy bacteria, viruses, and any other foreign bodies with the help of macrophages. When a body is fighting infection, the lymphocytes multiply rapidly and produce swelling of the lymph nodes. Extended swelling, therefore, is an indicator of a more complex infection which is also an early sign of oral cancer.
Lymph nodes are small bean-shaped glands throughout the body. They carry fluid, nutrients, and waste material between the tissues and bloodstream. Your doctor should check the swollen lymph nodes (generalized lymphadenopathy) that don’t go away within a month.
Sinus Infections
Sinus infections affect the tissue in the paranasal sinus, which is a bone of the skull or face. Infections in the sinus are rare, and persistent infections are a known sign of oral cancer.
Sinusitis occurs when sinus infection occurs when your nasal cavities and nasal passages become swollen or inflamed. Relentless pressure and swelling in the sinuses can cause headaches, earaches, toothaches, and pain in jaws and cheeks.
Pain in The Eye
Eye infections are also common to people without being a sign of oral cancer. However, a persistent eye infection is also one of the signs of oral cancer.
According to the MedlinePlus encyclopedia, Eyes pain is described as a burning, throbbing, aching, or stabbing sensation in and around the eye. Eye pain is a regular condition without serious conditions. However, persistent eye pain may result from sinuses infection or, to some extent, may be caused by oral cancer.
Persistent Bad Breath
Bad breath is a common phenomenon to many people in their lifetime, which may not necessarily mean it’s a sign of cancer. But persistent bad breath that worsens and generally happens often due to illness is another major sign of oral cancer.
Bad breath (halitosis or malodor or femoris) can be embarrassing and tough on those around one. Bad breath can be attributed to bronchiectasis, bronchitis, gum diseases, tooth decay, tonsillitis, and sinusitis. Regular dental checkups should be done to ensure oral hygiene is picked up and treated early.
Difficulty Moving Jaw or Tongue
Jaw and tongue movements should always be smooth and not painful or difficult. Difficulty in jaw movement for a prolonged time is a sign of serious cause or infection, one of them being oral cancer. Jaw joints (temporomandibular joints) are crucial for normal mouth opening, eating, and talking. Temporomandibular disorders are one of the symptoms of oral cancer.
Prolonged Hoarseness
Prolonged hoarseness of voice, especially caused by years of smoking tobacco and sometimes from dip (chewing), is another most common warning sign of oral cancer.
Therefore, having a dry, harsh voice calls for doctor review to determine the cause and its impacts on one’s health. Hoarseness is an abnormal change in your voice. One should seek doctor advice on chronic or prolonged hoarseness.
Persistent Oral Thrush
Oral thrush occurs when yeast infections develop inside the mouth or tongue. Oral thrust is a mild infection that rarely causes complications, but it can be problematic when there is a weakened immune system. Persistent oral thrush is also a symptom of advanced oral cancer.
Trending Health Topics
- ADHD
- Allergies
- Arthritis
- Bipolar Disorder
- Bunions
- Car Accidents
- Chron's Disease
- Common Cold
- COPD
- Depression
- Dry Skin
- Dry throat
- Eczema
- Fungal Infection
- GERD
- HIV/AIDS
- Hypertension
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriasis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Skin Disorders
- strep throat
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Uncategorized