Hyperthyroidism - Symptoms, Treatment, Causes and Diagnosis
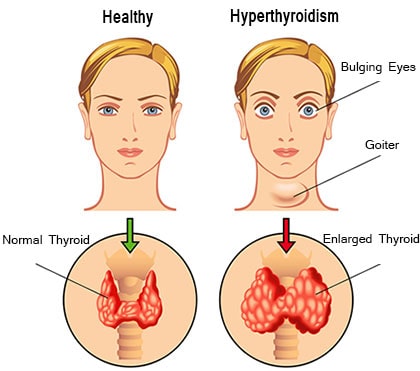
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland becomes overreactive thus producing excess thyroxine hormone.
The overproduction of thyroxine hormone accelerates the body’s metabolic processes causing anxiety, excessive sweating, weight loss, and many other symptoms.
The thyroid gland is a butterfly-shaped gland at the front of your neck. Its primary function is producing hormone thyroxine, which controls several body functions like heartbeat and metabolism.
This disease can successfully be treated and the patient recovers as expected if appropriate diagnosis and medication are applied.
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
There are several possible causes of hyperthyroidism. The commonly known causes are;
Graves’ Disease
Graves’ disease is an autoimmune disorder that causes the thyroid gland to overproduce thyroxine hormone. This is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. This disease is hereditary and it is common in women than in men.
Thyroiditis
This is the inflammation of the thyroid gland. This disorder can trigger thyroid cell damage thus causing thyroxine hormone to leak and this increases its level in the blood.
Excess Iodine
Studies have shown that people who consume too much iodine from foods or supplements or taking medications containing iodine have a higher risk of overproducing thyroxine hormone.
Tumors in The Ovaries or Testes
Some disease that causes tumors in the ovaries and testes can make the thyroid gland to be over-stimulated thus causing hyperthyroidism.
Thyroid Nodules
Thyroid nodules can produce thyroxine hormone thus causing excess hormone in the body. This causes the symptoms of hyperthyroidism to show up.
Signs and Symptoms
Some people might not experience any symptoms until the disease is in the advanced stage. The symptoms mostly delay in adults and only weight loss will be witnessed.
The common signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism are;
- Excessive sweating
- Nervousness and irritability
- Tremor
- Sleeping difficulties
- Weight loss
- Increased appetite
- Fatigue and muscle weakness
- Thyroid enlargement
- Increased bowel movements
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland
- Increased heat sensitivity
- Increased heart palpitations or heart rate
- Thin and delicate skin
- Eye irritation
- Irregular menstruation periods
- Fine, brittle hair
- Mental disturbances.
Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism
The doctor will perform several tests to determine if the patient is really suffering from hyperthyroidism. Some of the diagnostic procedures are;
Physical Exam
The doctor will try assessing for the signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism in the patient. They will also check the patient’s medical history in order to get any possible links of symptoms having been caused by some medications or diseases.
Hormone and Antibody Blood Test
This test is used to determine the levels of thyroxine and thyroid-stimulating hormone(TSH) in the blood. High levels of thyroxine and low or even nonexistent amounts of the thyroid-stimulating hormone will indicate the thyroid gland is overactive. TSH is a hormone that plays a greater role in the production of thyroxine hormone and this is why checking for its levels is of importance.
Ultrasound
This test can be used to evaluate the presence of lumps, nodules or enlargement of the thyroid gland. It will also show whether the thyroid nodules or lumps are solid or fluid-filled. This test will not show if you have hyperthyroidism but it will help in showing some of the possible symptoms associated with it such as the thyroid nodules and lumps.
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI)
This will be used to provide a detailed visualization of your thyroid glands. It will show whether they are enlarged and it will also reveal any possible defects in it. This method will also not show directly that you are suffering from hyperthyroidism.
CT Scan
This test will also be used to evaluate the size of your thyroid gland though, it will also not show directly if you have hyperthyroidism.
Radioactive Iodine Uptake
This test is used to determine iodine intake by the thyroid gland. You will be given a small oral dose of radioactive iodine then it will be tested to see how much has collected in the thyroid gland after 4 or 6 or 24 hrs. If too much iodine is collected then it will indicate you have hyperthyroidism.
Fine Needle Aspiration Biopsy
In this test, a small tissue is removed from the thyroid gland and taken for testing.
Treatment of Hyperthyroidism
The several methods that can be used in the treatment of hyperthyroidism are;
Antithyroid Drugs
The commonly used drugs for the treatment of hyperthyroidism are Thionamides. Drugs classified as Thionamides are; carbimazole, methimazole, and propylthiouracil. These drugs will help in controlling hyperthyroidism. These drugs can be administered through titration or block and replace methods. The effect of this medication is its possibility of causing agranulocytosis (which is the suppression of the production of white blood cells in the bone marrow)
Radioactive Iodine
This is the most used treatment method for hyperthyroidism. It is regarded as the safest of all. It helps in reducing the production of thyroxine hormone and can also reduce the size of the thyroid gland. It is regarded as a permanent treatment method. Some of the side effects can include; having a metallic taste in your mouth and mild feelings of nausea and vomiting.
Limited Iodine Food
Reducing iodine consumption can help in lowering the effects of hyperthyroidism. Though this method will not eliminate the disease in most cases, it will help in setting a base for other treatments to be successful.
Surgery / Thyroidectomy
This is also an alternative treatment for hyperthyroidism but it is not widely used. A small portion of the affected thyroid gland is removed. This method can cause damage to surrounding tissues during the surgery process.
Trending Health Topics
- ADHD
- Allergies
- Arthritis
- Bipolar Disorder
- Bunions
- Car Accidents
- Chron's Disease
- Common Cold
- COPD
- Depression
- Dry Skin
- Dry throat
- Eczema
- Fungal Infection
- GERD
- HIV/AIDS
- Hypertension
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriasis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Skin Disorders
- strep throat
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Uncategorized