What is a Heart Attack
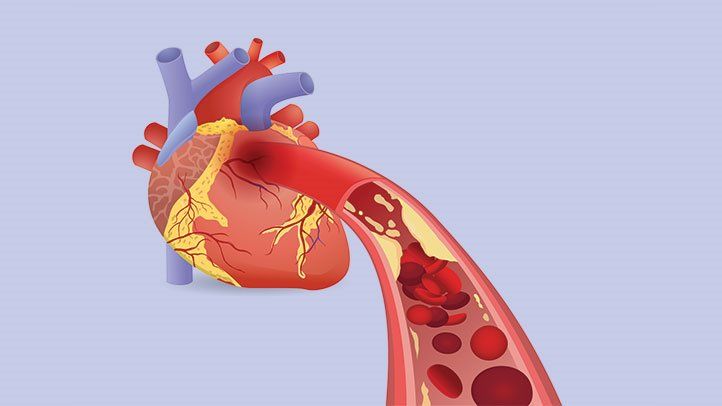
Heart attack arises when the bloodstream to any portion of the heart is disturbed, causing some heart cells to die. These commonly occur due to blockage or occlusion of a coronary artery. Decreased blood supply leads to a shortage of oxygen causes excessive damage or death called infarction in the heart muscle tissues that is the myocardium, it can lead to a massive heart attack.
Causes and Risk Factors of Massive Heart Attack
Age over forty in men fifty in women, excessive smoking, high blood pressure, tension, previous history of heart attack, low levels of high-density lipoprotein, obesity, excessive alcohol intake, chronic kidney disease, diabetes, anxiety, and stress. Medical conditions such as blockage of the major artery such as a coronary artery, teeth filling because filling material contain mercury it will penetrate in your blood leads to massive heart attack, ventricular fibrillation or arrhythmic patient, coronary artery patient, drug addiction patient, increased level of cholesterol in your blood, and hyperhomocysteinemia.
Symptoms of Massive Heart Attack
Breathing problem, change in the heart rate, obfuscation, weakness in the muscle, shivering, fatigue, chest pain it extending to the left arm or left side of shoulder and neck, pulse, nausea, vomiting, sweating, anxiety these are primarily seen in men, shortness of breath, feeling of indigestion, weakness, and fatigue these are seen in women. Most people can die due to massive heart attacks. Low fever, pale skin, severe distress, and restlessness, increased or decrease blood pressure, leg swelling, irregular pulse rate, heart enlargement, and hepatojugular reflux.
Diagnosed By
History collection about the habit previous history of this disease and history of heart attack, physical examination, chest X-ray to rule out swelling heart, echocardiogram, electrocardiogram, a coronary angiogram to rule out any obstructions on the heart vessels, thallium miller test to identify blood supply of the heart, blood test includes hemoglobin level, bleeding time and clotting time, blood cholesterol level, TC, DC, ESR, as well as Technetium-99m 2-methoxyisobutylisonitril.
Treatment For Massive Heart Attack
Anti-Platelet Therapy
To reduce the heart risk, anti-platelet therapy can be applied. Anti-platelet treatment split up those fat elements, which play an insignificant role in causing blood clotting inside the heart, which in turn causes a massive heart attack in the individual. To use this, antiplatelet therapy such as aspirin is administered to the heart disease patient, mixing with the clopidogrel medicine. Before giving the antiplatelet treatment, the patient should consult the consultant and discuss its feasibility, as it happens to be risky for a few patients susceptible to different diseases.
Beta-Blocker Therapy
This is a therapy used to supply the clotted heart with plasma to put the disorderly function of the heart onto its natural heart track. It is primarily used on high-risk heart attack patients such as those with a disease of ventricular dysfunction and continuing cardiac ischemia.
ACE Inhibitor Therapy
This therapy is used on those patients who are already affected with a massive heart attack look like to die any time. It will help to reduce heart failure and reductions of ventricular restoration. This type of treatment should be given within 24 to 48 hours after the occurrence of a massive heart attack.
Statin Therapy
It helps to reduce the risks of massive heart attacks leading to morbidity and death after the heart attack.Omega-3 Fatty Acids-It is usually found in fish decreases the chances of death following a massive heart attack. It reduces the risks of fatal arrhythmias. Other Remedial Treatments include oxygen administration, administering pain killers such as morphine sulfate, NTG, or nitroglycerin, providing adequate rest, providing a com environment, and avoiding heavy work.
Trending Health Topics
- ADHD
- Allergies
- Arthritis
- Bipolar Disorder
- Bunions
- Car Accidents
- Chron's Disease
- Common Cold
- COPD
- Depression
- Dry Skin
- Dry throat
- Eczema
- Fungal Infection
- GERD
- HIV/AIDS
- Hypertension
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriasis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Skin Disorders
- strep throat
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Uncategorized