Symptoms Causes and Treatment For Gallstones
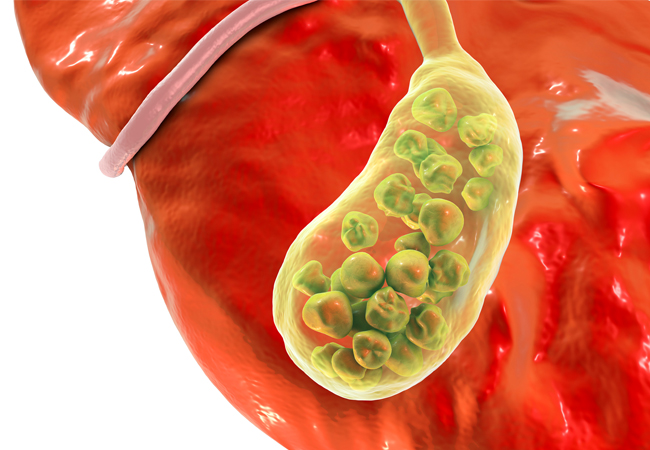
Function Of The Gallbladder
Bile is a bitter greenish-yellow fluid made in the liver and sent to the gallbladder where it is stored. Upon eating, it is sent to the intestines to aid in breaking down fats during digestion.
Symptoms of Gallbladder Disease
Gallstones affect women and over 40 more than any other group; it is a common problem worldwide. In many instances, there are no symptoms. Gallstones are hard deposits that form in the gallbladder. They can be as small as a grain of sand up to the size of a golf ball. They can block the bile duct causing pain, fever, or infection (Cholecystitis).
Symptoms can include:
- Gas
- Bad breath in combination with other symptoms
- Frequent burping after meals
- Bloating
- Gas
- Indigestion
- Chest pain
- Nausea
- Stomach pain
- Back pain
- Heartburn symptoms
- Vomiting
- Pain after eating
- Fever and chills
- Jaundice (a yellow or orange discoloration of the skin/eyes) is sometimes called Icterus.
- Pale colored stools
- Yellow skin
- Yellow eyes
- Sweating
- Pain 3-5 inches below the lower right rib
- Pain or discomfort in the abdominal area after meals
- Diarrhea
- Dark urine
- Rapid heartbeat
- Drop-in blood pressure
Causes Of Gallstones
They’re two primary types of gallstones cholesterol and pigment. Cholesterol stones are formed if there is an imbalance (excess) of either cholesterol or bilirubin and insufficient bile salts.
Pigment stones are more common among those with:
- Cirrhosis
- Hemolytic Anemia(abnormal breakdown of the red blood cells)
- Hereditary blood disorders like sickle cell anemia
- Biliary tract infections
Stone coloration range from black to brown, which forms when too much bilirubin is in the bile.
Other Factors to Consider
- Age
- Race
- Sex
- Diet
- Genetic or hereditary disorders
- Weight
Another point of interest would be how often and completely the gallbladder empties itself so the levels of bile do not become over-concentrated and create stones.
Medical Options
In terms of treatment, one option is to dissolve the stones with drugs like Ursodeoxycholic acid, Chenix, or Actigall. Drug therapy can take a few months or up to 2 years. Once the treatment is stopped, the gallstones may return.
A second option is a surgery (Laparoscopic Cholecystectomy) to remove the gallbladder.
Alternative Treatments
These may include a gallbladder or liver flush.
Testing Diagnosis
Suppose you think but are unsure if you have gallstones. See your doctor. They will be able to perform testing, including an abdominal ultrasound scan to get more information about the liver, pancreas, and gallbladder condition.
Another alternative is the cholecystogram, where iodine dyes are injected into a vein or pills are given, and x-rays are taken to shed light on the behavior of the gallbladder.
Trending Health Topics
- ADHD
- Allergies
- Arthritis
- Bipolar Disorder
- Bunions
- Car Accidents
- Chron's Disease
- Common Cold
- COPD
- Depression
- Dry Skin
- Dry throat
- Eczema
- Fungal Infection
- GERD
- HIV/AIDS
- Hypertension
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriasis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Skin Disorders
- strep throat
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Uncategorized