Burns Cause and How to Treat a Minor Burn?
Burns is the type of skin injury that is either a minor medical issue manageable with home treatment or a life-threatening condition requiring immediate medical help. The severity of burns is classified according to the depth of the affected tissue from which also depends on the symptoms ranging from red, swollen skin, and mild pain to serious internal injury and even death.
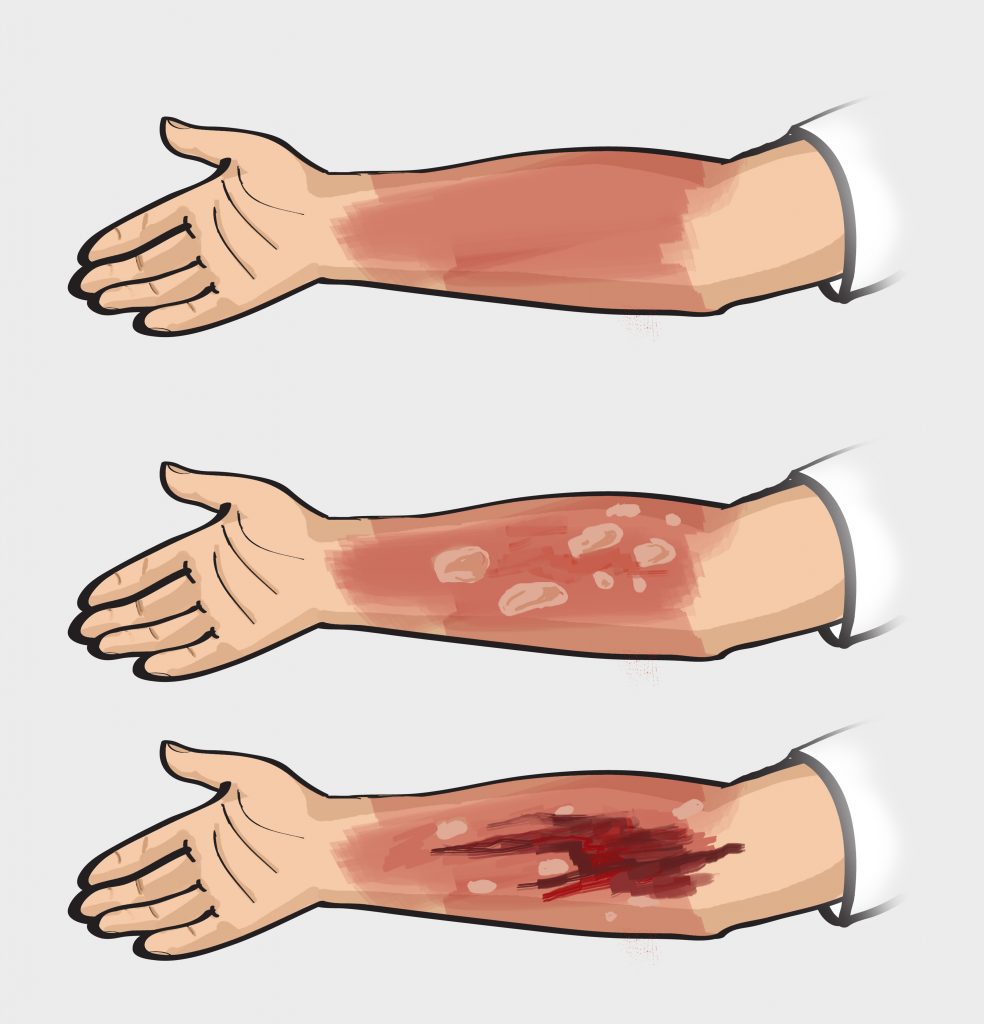
Milder cases classified as first-degree burns are characterized by red, swollen skin and moderate to severe pain and typically resolve with first-aid measures within few days. Very common are also second-degree burns that affect the first two layers of the skin (epidermis and dermis) and are characterized by moist-looking skin, severe pain, and blistering and scarring. The severest types of burns are third-degree and fourth-degree burns reaching the tissue beneath the skin and requiring immediate medical assistance.
Burns are caused by exposure of the skin to high temperatures – higher than 60 °C (140 ºF) and various substances, including chemicals, ultraviolet light, radiation, electricity, and friction. Most cases of burns are caused by heat involving fire, hot liquids (hot baths and spilled hot drinks), or steam, but the majority of people are also familiar with sunburns, a type of radiation burns caused by overexposure to sunlight. Radiation burns can also be caused by exposure to ultraviolet light from tanning booths and sunlamps and radiation from x-rays and radiation therapy used for cancer treatment. Radiation burns can also occur in nuclear fallout, but this radiation burn is fortunately very rare.
Friction burns are a type of burns caused by heat generated by friction when the skin rubs against another surface such as rope, carpet, or any other abrasive surface, including a person’s own skin.
Electrical burns are caused by electric shock and do not necessarily result in any visible tissue damage. However, electric shock can cause serious internal injuries and even death. Most cases of electrical burns occur at home involving misuse or defects of various household appliances such as electric sockets, plugs, lighting fittings, toasters, extension leads, washing machines, hair driers, etc. Lightning is also a type of electric burn, but it is scarce.
Chemical burns often resulting in severe tissue damage are caused by skin contact with chemicals such as strong acids and bases. Chemical burns occur either immediately on contact or are not immediately noticeable but are typically very painful. This type of burn does not need a source of heat.
How to Treat a Minor Burn?
You need to determine the type of burn before looking for a treatment. There are three types of classified burns.
1st-Degree Burn
There are three layers of the human skin. If only the outer layer is burned, it is known as 1st-degree burn. Symptoms of this burn are given below. Sunburn is the most common example of 1st-degree burn.
- Skin becomes red
- Swelling is there on the skin
- It can be painful
2nd-Degree Burn
If the burn reaches the second layer of skin, it is called 2nd – degree burn.
Symptoms:
- Blisters can be seen on the skin
- Skin takes the red and splotchy appearance
- Pain and swelling is also witnessed
3rd-Degree Burn
It involves all layers of skin and is very dangerous. It can cause permanent tissue damage. The burned area appears white and dry. It affects muscles, fats, and even bones. It can cause difficulties in inhaling and exhaling if there is smoke inhalation in a burn.
The first action after the burn is based upon the type of burns. Two types include minor and major. 1st-degree burns and 2nd-degree burns are treated as minor, and third-degree burns are treated as major burns.
For a minor burn, you are supposed to take the following actions:
- Cool the burn – You should cool down the burned area under cold water for 10 to 15 minutes. You should use water only. Ice should be avoided. Cooling down reduces the swelling of the burn. It conducts the heat of burned skin by conducting it away.
- Use a sterilized bandage to cover it – Avoid using cotton to cover the burn. Do not put too much pressure while wrapping the gauge. It will keep the air away and reduce the pain. It also protects the skin from blisters.
- Take any pain reliever – Take aspirin, ibuprofen, or naproxen as soon as possible. It would be best if you always read the cautions before using them.
For major burns, you should call emergency help as soon as possible.
You should follow some steps until emergency arrives:
- You should not remove burned clothes. Make sure that the victim is no more in contact with smoke or heat.
- Never use cold water in case of these big burns. It will lower down the body temperature. It affects circulation.
- Keep checking the circulation signs.
- It would be best if you covered the burned area.
1st-degree burns are the most common. You can have them in your daily life.
Therefore, here are some instructions were given to treat the 1st-degree burns:
- It would be best if you cooled it down under running water. The water should be cold.
- You can take ibuprofen to stop the swelling and pain. If the burn is tiny, do not take any medicine.
- Rub the burned area with petroleum jelly. Do it gently.
- It would be best if you wrapped it with a gauge. Do not wrap it with pressure. It will give you pain otherwise. Germs won’t be able to touch the burned area this way.
Trending Health Topics
- ADHD
- Allergies
- Arthritis
- Bipolar Disorder
- Bunions
- Car Accidents
- Chron's Disease
- Common Cold
- COPD
- Depression
- Dry Skin
- Dry throat
- Eczema
- Fungal Infection
- GERD
- HIV/AIDS
- Hypertension
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome (IBS)
- Multiple Sclerosis
- Osteoarthritis
- Psoriasis
- Rheumatoid Arthritis
- Skin Disorders
- strep throat
- Type 2 Diabetes
- Uncategorized