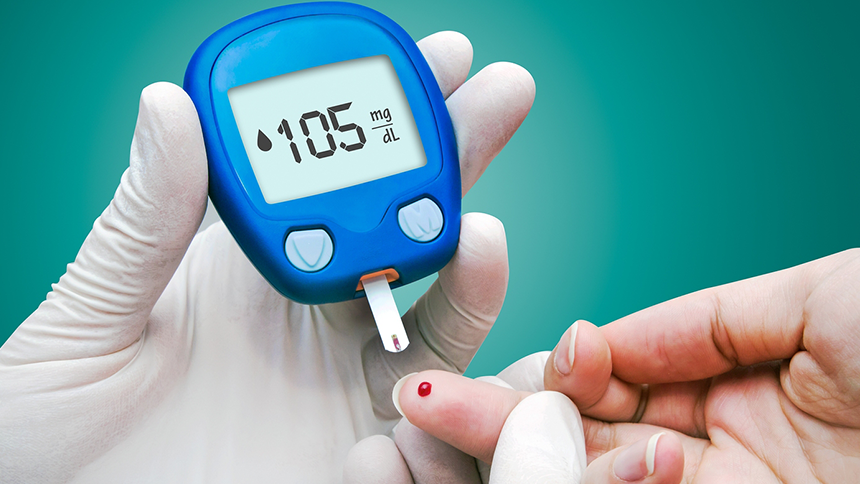
Today the technology has gone past just the hospitals. It was long ago when people needed to go to the hospitals to do a blood pressure check or even check monitor and check their blood glucose levels. Today there are many devices and blood glucose meters which people have at home, through which they can measure and monitor the sugar levels in the blood at home. There a however a few basics of Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose which people should be aware of.
Why is it Vital to Monitor The Glucose Level in The Blood?
For a normal healthy person who does not have diabetes it is not important at all. But for those who have diabetes, the sugar levels that are out of control can lead to severe conditions such as loss of memory, organ disorders, hyperglycemia, hypoglycemia, etc. In many severe conditions if the person does not monitor and control sugar levels it can lead to brain damage, organ failure, loss of eyesight, etc.
What is SMBG?
The SMBG or self monitoring blood glucose is a practice to test the blood for glucose levels at home. The people who have diabetes perform the blood glucose test. With the test at home, the person can know the changes in the sugar levels. Once these levels are monitored the person then relates the results to a blood glucose chart. This chart has the information about various levels and what to do if the levels rise or fall below the average. Today many people after carrying out the test at home use these charts to monitor and manage their diabetes.
What is The Purpose of SMBG?
The purpose of taking a blood glucose test at home is to know the patterns of blood glucose so that the patient can plan the diet, meals, and activities accordingly. In many cases it also helps patients know when to take the medicine and when to avoid it. Testing also allows giving a quick response in case of high or low glucose levels. In short these are the reasons to test:
- See if the treatment for diabetes is working or not?
- Monitor the affect of medication
- Change the medication or activity depending on the results
- Blood glucose monitor in case of illness or other disease
- Understand how diet affects the diabetes
Self-Monitoring of Blood Glucose (SMBG) involves regular testing of blood sugar levels using a glucometer. This helps people with diabetes to track their blood sugar levels and adjust their insulin doses if necessary. The following are the basics of SMBG:
- Timing: SMBG should be done at regular intervals, as advised by a healthcare provider, depending on type of diabetes and medication.
- Equipment: A glucometer, lancets, and test strips are needed for SMBG.
- Procedure: A small drop of blood is obtained from a finger or alternative site and placed on a test strip which is then inserted into the glucometer for reading.
- Record Keeping: Keeping track of the results helps in identifying patterns and trends in blood sugar levels, and makes it easier for healthcare providers to adjust treatment plans.
- Limitations: SMBG is a snapshot of the blood sugar level at a particular moment and may not always reflect overall glucose control. Other factors such as stress and illness can also affect results.
- Importance: Regular SMBG helps people with diabetes to maintain good glucose control, avoid complications and lead a healthy life.
How Many Times Should a Person Test?
For a person who has been diagnosed with type-1 diabetes, the doctor will recommend him to test at least 4 and at maximum 8 times in a day. Test before meals and after meals, one time when a person wakes up in the morning (before and after taking medicine) and one time before sleeping (after taking medication). The person who has type-2 diabetes who also takes insulin can test only two or three times a day.
The range of tests also differs in women and men. The self-monitoring blood glucose is different for pregnant woman and those who are not. It is different also for different age groups.